分布式计算
Ignite 可以以分布式、负载平衡和容错的方式在集群上运行业务代码。
任务可以在单节点、多节点或整个集群上运行,并且可以选同步和异步方式执行。
提示
Ignite 计算引擎现在支持在 Java 和 .NET 中实现的作业。由于 .NET 计算作业需要一些额外的配置,具体请参见 .NET 计算作业章节的内容。
除了标准计算任务外,Ignite 还支持并置执行,即任务可以直接在持有其所需数据的节点上运行,从而减少网络开销并提高性能。集群还支持 MapReduce 任务,可以高效处理大型数据集。这时任务将在持有其所需数据的节点上执行。
在节点之间发送代码和数据时,对象会转换为可传输的格式,以便可以准确地重建。Ignite 会自动处理元组、POJO 和原生类型等常见类型的编组,但对于更复杂或自定义的对象,可能需要实现自己的编组逻辑。
1.计算作业代码部署
在提交计算作业之前,先须将代码部署到目标节点。
如果使用的是嵌入式节点,则项目类路径中包含的任何代码也会被计算作业依赖。
2.配置作业
Ignite 中计算作业由两个关键组件定义:JobTarget和JobDescriptor,这些组件确定作业将在哪些节点上运行以及作业的结构,包括输入和输出类型、编组器以及表示作业的部署类。
2.1.JobTarget
在提交作业之前,必须创建一个JobTarget对象来指定哪些节点将执行作业。作业目标可以指向某个节点,集群上的任何节点,或在持有指定数据的节点上执行并置计算作业,可用的方法如下:
JobTarget.anyNode():作业将在任何节点上执行;JobTarget.node():作业将在特定节点上执行;JobTarget.colocated():作业将在持有指定数据的节点上执行。
提示
如果要跨多个节点执行作业,请改用BroadcastJobTarget对象。
2.2.JobDescriptor
JobDescriptor对象包含作业执行所需的所有细节,必须提供以下参数:
- 作业描述符是使用构建器创建的,其会指定作业参数的输入类型、预期输出类型以及要执行的作业类的全限定名;
units表示部署单元,其可以使用单元的名称创建,并指定Version.LATEST,使作业始终运行在最新部署的版本;resultClass指定预期结果类型,以便系统可以正确处理作业的输出;argumentMarshaller和resultMarshaller定义如何序列化作业的输入参数和输出结果。对于常见类型,可以省略该编组器并传递null给构造器,因为 Ignite 会自动处理序列化。
下面的示例假设NodeNameJob类已经部署到对应的节点。
- 如果使用常见类型,则无需定义自定义编组器,Ignite 会自动处理。以下示例演示了使用内置编组器的简化作业描述符:java
String result = client.compute().execute( JobTarget.anyNode(client.cluster().nodes()), JobDescriptor.builder(WordPrintJob.class) .units(new DeploymentUnit(DEPLOYMENT_UNIT_NAME, DEPLOYMENT_UNIT_VERSION)) .resultClass(String.class) .build(), "Hello, Ignite!" ); - 下面的示例演示如何为自定义
MyJobArgument的作业创建自定义作业描述符,该作业在随机集群节点上运行,并使用自定义编组器返回MyJobResult对象:javaMyJobResult result = client.compute().execute( JobTarget.anyNode(client.cluster().nodes()), JobDescriptor.<MyJobArgument, MyJobResult>builder(WordPrintJob.class) .units(new DeploymentUnit(DEPLOYMENT_UNIT_NAME, DEPLOYMENT_UNIT_VERSION)) .resultClass(MyJobResult.class) .argumentMarshaller(new ArgMarshaller()) .resultMarshaller(new ResultMarshaller()) .build(), new MyJobArgument("Hello, Ignite!") );
2.3.部署单元信息
JobExecutionContext对象包含有关作业所在的部署单元的信息,其持有一个DeploymentUnitInfo集合。
每个DeploymentUnitInfo对象提供以下信息:
name():部署单元的名称;version():部署单元的版本;path():部署单元内容的文件系统路径。
public class DiagnosticJob implements ComputeJob<Void, String> {
@Override
public CompletableFuture<String> executeAsync(JobExecutionContext context, Void input) {
// Access deployment unit information
String deploymentInfo = context.deploymentUnits().stream()
.map(unit -> String.format("%s:%s at %s",
unit.name(),
unit.version(),
unit.path()))
.collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(deploymentInfo);
}
}3.执行作业
Ignite的计算作业,可以在某个节点、任意节点、或者使用并置的方式,即作业在持有相关数据的节点上执行。
3.1.单节点执行
有时可能需要在集群中的某个节点上执行作业,做法有如下几种:
submitAsync():将作业发送到集群,并返回一个Future,当提交作业执行时,该Future将与JobExecution对象一起完成;executeAsync():将作业发送到集群,并返回一个Future,该Future将在作业执行结果准备就绪时完成;execute():将作业发送到集群并等待作业执行的结果。
try (IgniteClient client = IgniteClient.builder()
.addresses("127.0.0.1:10800")
.build()
) {
System.out.println("\nConfiguring compute job...");
JobDescriptor<String, Void> job = JobDescriptor.builder(WordPrintJob.class)
.units(new DeploymentUnit(DEPLOYMENT_UNIT_NAME, DEPLOYMENT_UNIT_VERSION))
.build();
JobTarget jobTarget = JobTarget.anyNode(client.clusterNodes());
for (String word : "Print words using runnable".split(" ")) {
System.out.println("\nExecuting compute job for word '" + word + "'...");
client.compute().execute(jobTarget, job, word);
}
}ICompute compute = Client.Compute;
IList<IClusterNode> nodes = await Client.GetClusterNodesAsync();
IJobExecution<string> execution = await compute.SubmitAsync(
JobTarget.AnyNode(nodes),
new JobDescriptor<string, string>("org.example.NodeNameJob"),
arg: "Hello");
string result = await execution.GetResultAsync();using namespace ignite;
compute comp = client.get_compute();
std::vector<cluster_node> nodes = client.get_nodes();
// Unit `unitName:1.1.1` contains NodeNameJob class.
auto job_desc = job_descriptor::builder("org.company.package.NodeNameJob")
.deployment_units({deployment_unit{"unitName", "1.1.1"}})
.build();
job_execution execution = comp.submit(job_target::any_node(nodes), job_desc, {std::string("Hello")}, {});
std::string result = execution.get_result()->get<std::string>();3.2.多节点执行
要在多个节点上执行计算任务,方法与前述单节点执行的相同,不同点在于,无需创建JobTarget对象来指定执行节点,而是使用BroadcastJobTarget并指定执行任务的节点列表。
该BroadcastJobTarget对象可以指定以下内容:
BroadcastJobTarget.nodes():作业将在列表中的所有节点上执行。BroadcastJobTarget.table():作业将在持有指定表的分区的所有节点上执行。
可以通过设置节点列表来控制在哪些节点上执行任务。
try (IgniteClient client = IgniteClient.builder()
.addresses("127.0.0.1:10800")
.build()
) {
System.out.println("\nConfiguring compute job...");
JobDescriptor<String, Void> job = JobDescriptor.builder(HelloMessageJob.class)
.units(new DeploymentUnit(DEPLOYMENT_UNIT_NAME, DEPLOYMENT_UNIT_VERSION))
.build();
BroadcastJobTarget target = BroadcastJobTarget.nodes(client.cluster().nodes());
System.out.println("\nExecuting compute job...");
client.compute().execute(target, job, "John");
System.out.println("\nCompute job executed...");
}ICompute compute = Client.Compute;
IList<IClusterNode> nodes = await Client.GetClusterNodesAsync();
IBroadcastExecution<string> execution = await compute.SubmitBroadcastAsync(
BroadcastJobTarget.Nodes(nodes),
new JobDescriptor<object, string>("org.example.NodeNameJob"),
arg: "Hello");
foreach (IJobExecution<string> jobExecution in execution.JobExecutions)
{
string jobResult = await jobExecution.GetResultAsync();
Console.WriteLine($"Job result from node {jobExecution.Node}: {jobResult}");
}using namespace ignite;
compute comp = client.get_compute();
std::vector<cluster_node> nodes = client.get_nodes();
// Unit `unitName:1.1.1` contains NodeNameJob class.
auto job_desc = job_descriptor::builder("org.company.package.NodeNameJob")
.deployment_units({deployment_unit{"unitName", "1.1.1"}})
.build();
broadcast_execution execution = comp.submit_broadcast(broadcast_job_target::nodes(nodes), job_desc, {std::string("Hello")}, {});
for (auto &exec: execution.get_job_executions()) {
std::string result = exec.get_result()->get<std::string>();
}3.3.并置执行
Ignite中可以通过配置一个作业目标来执行并置计算,该作业目标指示任务在持有所需数据的节点上执行。
在下面的示例中,作业在持有特定分区的节点上执行,这些分区持有accounts表中主键accountNumber对应的行。这里将主键传递给JobTarget.colocated()以筛选节点,并将其作为作业参数,这样作业就知道要处理哪些数据:
try (IgniteClient client = IgniteClient.builder()
.addresses("127.0.0.1:10800")
.build()) {
System.out.println("\nConfiguring compute job...");
JobDescriptor<Integer, Void> job = JobDescriptor.builder(PrintAccountInfoJob.class)
.units(new DeploymentUnit(DEPLOYMENT_UNIT_NAME, DEPLOYMENT_UNIT_VERSION))
.build();
int accountNumber = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(ACCOUNTS_COUNT);
JobTarget jobTarget = JobTarget.colocated("accounts", accountKey(accountNumber));
client.compute().execute(jobTarget, job, accountNumber);
}string table = "Person";
string key = "John";
IJobExecution<string> execution = await Client.Compute.SubmitAsync(
JobTarget.Colocated(table, key),
new JobDescriptor<string, string>("org.example.NodeNameJob"),
arg: "Hello");
string result = await execution.GetResultAsync();using namespace ignite;
compute comp = client.get_compute();
std::string table{"Person"};
std::string key{"John"};
// Unit `unitName:1.1.1` contains NodeNameJob class.
auto job_desc = job_descriptor::builder("org.company.package.NodeNameJob")
.deployment_units({deployment_unit{"unitName", "1.1.1"}})
.build();
job_execution execution = comp.submit(job_target::colocated(table, key), job_desc, {std::string("Hello")}, {});
std::string result = execution.get_result()->get<std::string>();或者也可以通过创建BroadcastJobTarget.table()目标,在集群中持有某个表的分区的所有节点上执行计算作业,这时 Ignite 会自动找到持有某个表的分区的所有节点。
4.使用限定表名
如果未指定表模式,则默认使用PUBLIC模式。如果要使用其他的模式,需要使用全限定表名,可以使用一个字符串,也可以创建QualifiedName对象。
QualifiedName myTableName = QualifiedName.parse("PUBLIC.MY_QUALIFIED_TABLE");
String executionResult = client.compute()
.execute(
JobTarget.colocated(myTableName, Tuple.create(Map.of("k", 1))),
JobDescriptor.builder(NodeNameJob.class).build(),
null
);就像在单节点上执行一样,可以使用QualifiedName对象指定一个限定表名,并使用BroadcastJobTarget在多个节点上执行作业:
QualifiedName customSchemaTable = QualifiedName.parse("CUSTOM_SCHEMA.MY_QUALIFIED_TABLE");
client.compute().execute(BroadcastJobTarget.table(customSchemaTable), JobDescriptor.builder(HelloMessageJob.class).build(), null);还可以使用of方法分别指定表名和模式名:
QualifiedName customSchemaTableName = QualifiedName.of("PUBLIC", "MY_TABLE");
client.compute().execute(BroadcastJobTarget.table(customSchemaTableName), JobDescriptor.builder(HelloMessageJob.class).build(), null);这里的名字,必须符合标识符的SQL语法规则:
- 标识符必须以
Lu、L1、Lt、Lm、Lo或NlUnicode类别中的字符或U+0331(下划线)开头; - 标识符字符(第一个除外)可以是
U+00B7(中点),也可以是Mn、Mc、Nd、Pc或CfUnicode类别中的任何字符; - 包含任何其他字符的标识符必须用
U+2033(双引号)括起来; - 标识符内的双引号必须用2个双引号字符转义。
任何未被引用的名字都将被转换为大写,这时,Person和PERSON名称是等价的,否则就需在名称周围添加转义引号。例如,\"Person\"将被编码为区分大小写的Person名称。如果名称中包含U+2033(双引号)符号,则必须转义为""(2个双引号符号)。
5..NET计算作业
使用 .NET 编写的计算作业时,生成的二进制文件(DLL 文件)应部署到服务端节点,并由程序集限定的类型名调用。每个部署单元组合都加载到单独的 AssemblyLoadContext 中。
可以将同一作业(程序集)的多个版本部署到集群,因为 Ignite 支持部署单元的隔离。一个作业可以由多个部署单元组成,程序集和类型将按列出的顺序进行查找。
提示
.NET 计算作业在服务端节点上的单独进程(Sidecar)中执行。该进程在第一个.NET作业调用时启动,然后后续作业会复用。
计算作业类可以实现IDisposable和IAsyncDisposable接口, 不管成功还是失败,Ignite 都会在作业执行后调用Dispose或DisposeAsync。
5.1..NET 计算要求
- 每个服务端节点上都需要 .NET 8 运行时或更高版本(不是 SDK);
- 使用 ZIP包、DEB包、RPM 包安装时,必须自己安装 .NET 运行时。Ignite 的 Docker 镜像包括 .NET 8 运行时,因此可以在 Docker 中直接运行 .NET 作业。
5.2.实现 .NET 计算作业
下面是实现 .NET 计算作业的示例:
- 首先,使用
dotnet new classlib为作业实现准备一个类库项目。提示
在大多数情况下,最好为计算作业使用单独的项目来减小部署大小。
shelldotnet new classlib -n MyComputeJobs cd MyComputeJobs dotnet add package Apache.Ignite - 将对
Apache.Ignite包的引用添加到类库项目:shelldotnet add package Apache.Ignite - 然后创建一个实现
IComputeJob<TArg, TRes>接口的类,例如:csharppublic class HelloJob : IComputeJob<string, string> { public ValueTask<string> ExecuteAsync(IJobExecutionContext context, string arg, CancellationToken cancellationToken) => ValueTask.FromResult("Hello " + arg); } - 使用
dotnet publish -c Release命令发布项目:shelldotnet publish -c Release mkdir deploy cp bin/Release/net8.0/MyComputeJobs.dll deploy/ # Exclude Ignite assemblies; no subdirectories allowed ignite cluster unit deploy --name MyDotNetJobsUnit --path ./deploy - 将生成的 dll 文件和任何额外的依赖项复制到单独的目录,不包括
Apache Ignitedll。提示
包含 dll 的目录不得包含任何子目录。
- 使用Ignite的命令行
cluster unit deploy command命令将目录作为部署单元部署到集群,之后就可以运行了。
5.3.运行 .NET 计算作业
可以从任何客户端(.NET、Java、C++ 等)执行 .NET 计算作业,只要创建具有程序集限定作业类名的JobDescriptor,并使用JobExecutorType.DotNetSidecar配置JobExecutionOptions即可。
例如,下面是从 .NET 在单节点上运行作业的方法:
csharpvar jobTarget = JobTarget.AnyNode(await client.GetClusterNodesAsync()); var jobDesc = new JobDescriptor<string, string>( JobClassName: typeof(HelloJob).AssemblyQualifiedName!, DeploymentUnits: [new DeploymentUnit("MyDeploymentUnit")], Options: new JobExecutionOptions(ExecutorType: JobExecutorType.DotNetSidecar)); IJobExecution<string> jobExec = await client.Compute.SubmitAsync(jobTarget, jobDesc, "world");或者,使用
JobDescriptor.Of快捷方式从作业实例创建作业描述符:csharpJobDescriptor<string, string> jobDesc = JobDescriptor.Of(new HelloJob()) with { DeploymentUnits = [new DeploymentUnit("MyDeploymentUnit")] };可以从 .NET 代码调用 Java 计算作业,例如:
csharpIList<IClusterNode> nodes = await client.GetClusterNodesAsync(); IJobTarget<IEnumerable<IClusterNode>> jobTarget = JobTarget.AnyNode(nodes); var jobDesc = new JobDescriptor<string, string>(JobClassName: "org.foo.bar.MyJob", DeploymentUnits: [new DeploymentUnit("MyDeploymentUnit")]); IJobExecution<string> jobExecution = await client.Compute.SubmitAsync(jobTarget, jobDesc, "Job Arg"); string jobResult = await jobExecution.GetResultAsync();还可以从 Java 客户端运行 .NET 计算作业,例如:
javatry (IgniteClient client = IgniteClient.builder().addresses("127.0.0.1:10800") .build() ) { JobDescriptor<String, String> jobDesc = JobDescriptor.<String, String>builder().jobClassName("MyNamespace.HelloJob, MyComputeJobsAssembly").deploymentUnits(new DeploymentUnit("MyDeploymentUnit")).executionOptions(new JobExecutionOptions().executorType(JobExecutorType.DotNetSidecar)).build(); JobTarget jobTarget = JobTarget.anyNode(client.clusterNodes()); for (String word : "Print words using runnable".split(" ")) { System.out.println("\nExecuting compute job for word '" + word + "'..."); client.compute().execute(jobTarget, job, word); } }
6.使用限定表名
以下示例在集群中持有Person表分区的所有节点上执行相同的作业:
JobDescriptor<String, Void> job = JobDescriptor.builder(HelloMessageJob.class)
.units(new DeploymentUnit(DEPLOYMENT_UNIT_NAME, DEPLOYMENT_UNIT_VERSION))
.build();
BroadcastJobTarget target = BroadcastJobTarget.nodes(client.cluster().nodes());就像在单节点上执行一样,可以使用QualifiedName对象指定限定表名:
QualifiedName customSchemaTable = QualifiedName.parse("CUSTOM_SCHEMA.MY_QUALIFIED_TABLE");
client.compute().execute(BroadcastJobTarget.table(customSchemaTable), JobDescriptor.builder(HelloMessageJob.class).build(), null);还可以使用of方法分别指定表名和模式名:
QualifiedName customSchemaTableName = QualifiedName.of("PUBLIC", "MY_TABLE");
client.compute().execute(BroadcastJobTarget.table(customSchemaTableName), JobDescriptor.builder(HelloMessageJob.class).build(), null);提供的名称必须遵循标识符的 SQL 语法规则:
- 标识符必须以
Lu、L1、Lt、Lm、Lo或NlUnicode类别中的字符或U+0331(下划线)开头; - 标识符字符(第一个除外)可以是
U+00B7(中点),也可以是Mn、Mc、Nd、Pc或CfUnicode类别中的任何字符; - 包含任何其他字符的标识符必须用
U+2033(双引号)括起来; - 标识符内的双引号必须用2个双引号字符转义。
任何未被引用的名字都将被转换为大写,这时,Person和PERSON名称是等价的,否则就需在名称周围添加转义引号。例如,\"Person\"将被编码为区分大小写的Person名称。如果名称中包含U+2033(双引号)符号,则必须转义为""(2个双引号符号)。
7.工作归属
如果集群启用了身份验证,则计算作业将由某个用户执行。如果在集群上配置了用户权限,则用户需要适当的分布式计算权限才能执行分布式计算作业,只有具有JOBS_ADMIN权限的用户才能与其他用户的作业进行交互。
8.作业执行状态
使用异步API时,可以跟踪服务端上的作业状态,并对状态变化做出反应,例如:
public static void example() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
IgniteClient client = IgniteClient.builder().addresses("127.0.0.1:10800").build();
CompletableFuture<JobExecution<Void>> execution = client.compute().submitAsync(JobTarget.anyNode(client.cluster().nodes()), JobDescriptor.builder(WordPrintJob.class).build(), null);
execution.get().stateAsync().thenApply(state -> {
if (state.status() == FAILED) {
System.out.println("\nJob failed...");
}
return null;
});
System.out.println(execution.resultAsync().get());
}IList<IClusterNode> nodes = await Client.GetClusterNodesAsync();
IJobExecution<string> execution = await Client.Compute.SubmitAsync(
JobTarget.AnyNode(nodes),
new JobDescriptor<string, string>("org.example.NodeNameJob"),
arg: "Hello");
JobState? state = await execution.GetStateAsync();
if (state?.Status == JobStatus.Failed)
{
// Handle failure
}
string result = await execution.GetResultAsync();using namespace ignite;
compute comp = client.get_compute();
std::vector<cluster_node> nodes = client.get_nodes();
// Unit `unitName:1.1.1` contains NodeNameJob class.
auto job_desc = job_descriptor::builder("org.company.package.NodeNameJob")
.deployment_units({deployment_unit{"unitName", "1.1.1"}})
.build();
job_execution execution = comp.submit(job_target::any_node(nodes), job_desc, {std::string("Hello")}, {});
std::optional<job_status> status = execution.get_status();
if (status && status->state == job_state::FAILED)
{
// Handle failure
}
std::string result = execution.get_result()->get<std::string>();8.1.可能的状态和过渡
下图描述了作业状态的可能转换: 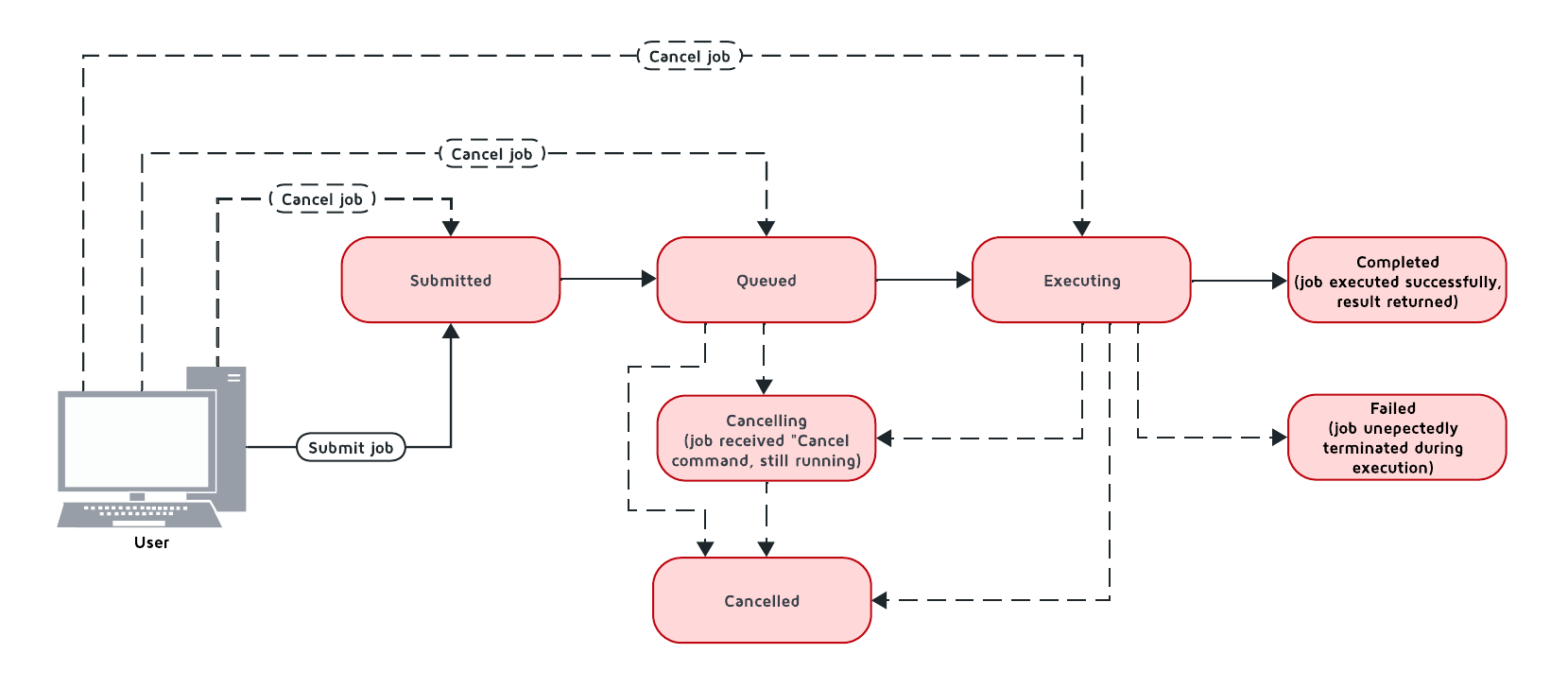
下表列出了支持的作业状态:
| 状态 | 描述 | 可过渡至 |
|---|---|---|
Queued | 作业已添加到队列中,并等待队列执行。 | Executing、Canceled |
Executing | 作业正在执行中。 | Canceling、Completed、Queued |
Completed | 作业执行成功,并返回执行结果。 | |
Failed | 任务在执行过程中意外终止。 | Queued |
Canceling | 作业已收到取消命令,但仍在运行。 | Completed、Canceled |
Canceled | 作业已成功取消。 |
如果所有任务执行线程都处于繁忙状态,则节点接收的新任务将根据其作业优先级放入任务队列中。Ignite 首先按优先级对所有传入的作业进行排序,然后按时间排序,首先执行较早排队的作业。
8.2.取消正在执行的作业
当节点收到处于Executing状态的任务的取消命令时,会立即向执行该任务的线程发送中断。通常这将导致作业立即被取消,但有时作业也可能会继续执行。如果发生这种情况,则作业将处于Canceling状态,根据正在执行的代码,作业可能会成功完成,在不间断操作完成后被取消,或者保持未完成状态(例如,如果代码卡在循环中)。可以使用JobExecution.stateAsync()方法跟踪作业所处的状态,并对状态更改做出反应。
为了取消计算作业,首先要创建CancelHandle并从中拿到一个令牌,然后可以使用此令牌取消计算作业:
CancelHandle cancelHandle = CancelHandle.create();
CancellationToken cancelToken = cancelHandle.token();
CompletableFuture<Void> execution = client.compute().executeAsync(JobTarget.anyNode(client.clusterNodes()), JobDescriptor.builder(NodeNameJob.class).build(), cancelToken, null);
cancelHandle.cancel();var cts = new CancellationTokenSource();
CancellationToken cancelToken = cts.Token;
var execution = client.Compute.ExecuteAsync(
JobTarget.AnyNode(await client.GetClusterNodesAsync()),
new JobDescriptor(typeof(NodeNameJob)),
cancelToken);
cts.Cancel();取消作业的另一种方法是使用 SQL 的 KILL COMPUTE 命令,可以通过COMPUTE_JOBS系统视图拿到作业的ID。
8.3.作业优先级
可以通过设置JobExecutionOptions.priority属性来指定作业优先级。优先级较高的作业将在优先级较低的作业之前排队(例如优先级为 4 的作业将在优先级为 2 的作业之前执行)。
public static void example() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
try (IgniteClient client = IgniteClient.builder().addresses("127.0.0.1:10800").build()) {
// Create job execution options
JobExecutionOptions options = JobExecutionOptions.builder().priority(1).build();
String executionResult = client.compute().execute(JobTarget.anyNode(client.cluster().nodes()),
JobDescriptor.builder(HighPriorityJob.class).options(options).build(), null
);
System.out.println(executionResult);
}
}var options = JobExecutionOptions.Default with { Priority = 1 };
IJobExecution<string> execution = await Client.Compute.SubmitAsync(
JobTarget.AnyNode(await Client.GetClusterNodesAsync()),
new JobDescriptor<string, string>("org.example.NodeNameJob", Options: options),
arg: "Hello");
string result = await execution.GetResultAsync();using namespace ignite;
compute comp = client.get_compute();
std::vector<cluster_node> nodes = client.get_nodes();
// Unit `unitName:1.1.1` contains NodeNameJob class.
auto job_desc = job_descriptor::builder("org.company.package.NodeNameJob")
.deployment_units({deployment_unit{"unitName", "1.1.1"}})
.build();
job_execution_options options{1, 0};
job_execution execution = comp.submit(job_target::any_node(nodes), job_desc, {std::string("Hello")}, std::move(options));
std::string result = execution.get_result()->get<std::string>();8.4.作业重试
可以通过设置JobExecutionOptions.maxRetries属性来设置作业失败时重试的次数。如果设置该参数,则失败的作业将在转到Failed状态之前重试指定的次数。
public static void example() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
try (IgniteClient client = IgniteClient.builder().addresses("127.0.0.1:10800").build()) {
// Create job execution options with maxRetries set to 5.
JobExecutionOptions options = JobExecutionOptions.builder()
.maxRetries(5)
.build();
String executionResult = client.compute().execute(JobTarget.anyNode(client.clusterNodes()),
JobDescriptor.builder(NodeNameJob.class).options(options).build(), null
);
System.out.println(executionResult);
}
}var options = JobExecutionOptions.Default with { MaxRetries = 5 };
IJobExecution<string> execution = await Client.Compute.SubmitAsync(
JobTarget.AnyNode(await Client.GetClusterNodesAsync()),
new JobDescriptor<string, string>("org.example.NodeNameJob", Options: options),
arg: "Hello");
string result = await execution.GetResultAsync();using namespace ignite;
compute comp = client.get_compute();
std::vector<cluster_node> nodes = client.get_nodes();
// Unit `unitName:1.1.1` contains NodeNameJob class.
std::vector<deployment_unit> units{deployment_unit{"unitName", "1.1.1"}};
job_execution_options options{0, 5};
job_execution execution = comp.submit(nodes, units, NODE_NAME_JOB, {std::string("Hello")}, std::move(options));
std::string result = execution.get_result()->get<std::string>();9.作业故障转移
Ignite 实现了一套机制来处理任务执行过程中发生的问题,处理以下情况:
9.1.工作节点下线
如果工作节点关闭,协调器节点会将分配给下线节点的所有作业重新分配给其他可用的节点。如果未找到则作业将失败,并将向客户端发送异常。
9.2.协调器节点下线
如果工作节点检测到协调器节点下线,所有作业都将被取消。注意,某些作业可能需要很长时间才能取消。
9.3.客户端断连
如果协调器节点检测到客户端断开连接,所有作业都将被取消。注意,某些作业可能需要很长时间才能取消。
10.MapReduce任务
Ignite 3 提供了一个 API,用于在集群中执行 MapReduce 操作,该操作会先拆分计算任务并分发在多个节点执行,然后汇总结果并将其返回给用户。
10.1.了解MapReduce任务
MapReduce 任务必须实现MapReduceTask接口,然后部署到对应的节点上才能执行。该接口提供了一种实现自定义映射和汇总逻辑的方法。接收任务的节点会成为协调器节点,该节点将负责将任务映射到其他节点,汇总其结果并将最终结果返回给客户端。
该类必须实现两个方法:splitAsync和reduceAsync。
splitAsync()方法负责根据输入参数创建计算作业并将其映射到工作节点。该方法接收执行上下文和任务的参数,并返回一个CompletableFuture,其中包含将发送到工作节点的作业描述符列表。
reduceAsync()方法在汇总步骤中,当所有作业都已完成时被调用。该方法从工作节点接收已完成的作业结果的映射,并返回计算的最终结果。
10.2.创建映射类
所有 MapReduce 作业都必须提交到部署了这些类的节点,下面是一个示例:
public static class PhraseWordLengthCountMapReduceTask implements MapReduceTask<String, String, Integer, Integer> {
/** {@inheritDoc} */
@Override
public CompletableFuture<List<MapReduceJob<String, Integer>>> splitAsync(
TaskExecutionContext taskContext,
String input) {
assert input != null;
var job = JobDescriptor.builder(WordLengthJob.class)
.units(new DeploymentUnit(DEPLOYMENT_UNIT_NAME, DEPLOYMENT_UNIT_VERSION))
.build();
List<MapReduceJob<String, Integer>> jobs = new ArrayList<>();
for (String word : input.split(" ")) {
jobs.add(
MapReduceJob.<String, Integer>builder()
.jobDescriptor(job)
.nodes(taskContext.ignite().cluster().nodes())
.args(word)
.build()
);
}
return completedFuture(jobs);
}
/** {@inheritDoc} */
@Override
public CompletableFuture<Integer> reduceAsync(TaskExecutionContext taskContext, Map<UUID, Integer> results) {
return completedFuture(results.values().stream()
.reduce(Integer::sum)
.orElseThrow());
}
}10.3.执行MapReduce任务
要执行 MapReduce 任务,请使用以下方法之一:
submitMapReduce():将 MapReduce 作业发送到集群,并返回可用于监控或修改计算任务执行的TaskExecution对象;executeMapReduceAsync():将 MapReduce 作业发送到集群,并返回作为作业执行结果的Future;executeMapReduce():将作业发送到集群并等待作业执行的结果。
try (IgniteClient client = IgniteClient.builder().addresses("127.0.0.1:10800").build()) {
System.out.println("\nConfiguring map reduce task...");
TaskDescriptor<String, Integer> taskDescriptor = TaskDescriptor.builder(PhraseWordLengthCountMapReduceTask.class)
.units(new DeploymentUnit(DEPLOYMENT_UNIT_NAME, DEPLOYMENT_UNIT_VERSION))
.build();
System.out.println("\nExecuting map reduce task...");
String phrase = "Count characters using map reduce";
Integer result = client.compute().executeMapReduce(taskDescriptor, phrase);
System.out.println("\nTotal number of characters in the words is '" + result + "'.");
}ICompute compute = Client.Compute;
var taskDescriptor = new TaskDescriptor<string, string>("com.example.MapReduceNodeNameTask");
ITaskExecution<string> exec = await compute.SubmitMapReduceAsync(taskDescriptor, "arg");
string result = await exec.GetResultAsync();
Console.WriteLine(result);18624049226
